06/15/2017
Humans are born with four hands, so to speak. Babies' feet are actually hands, shaped to hold, grasp, and climb, just like our closest relatives who still live in trees.
In order to raise his head above the animals, the little human has to become a biped. This important step, which took mankind millions of years to complete, only takes ten to 15 months. By the way, he doesn't need shoes, emphasizes the Children's Health Foundation in a statement.
"As delicate as they may look - baby's feet are strong enough to carry the weight of the body," says pediatrician Professor Dr. Berthold Koletzko, Chairman of the Children's Health Foundation. “Shoes are not necessary for their healthy development, on the contrary: shoes prevent the feet from touching and grasping. As a result, the child is deprived of important sensory stimuli and sensations and thus additional perception impulses for his brain. People only need shoes to protect themselves against cold, heat and injuries.” Many manufacturers offer their children's shoes in retail outlets and on the Internet under the designation “walking shoes”. The Children's Health Foundation emphasizes that no child needs shoes to learn to walk. Shoes are only appropriate when a child has learned to walk so well that it wants to be able to walk outside on its own feet.
Walking barefoot - a kick for head and feet
It is best for the child to start walking on their own soles - barefoot. Or - for example if the floor in the apartment is cold - on socks or in flexible slippers that have rubber nubs to prevent them from slipping. Your advantage: the feet move more freely and it is easy to see whether the socks fit. The Children's Health Foundation emphasizes that slippers also have to fit: According to current studies, around 80% of children wear slippers that are too short.
Professor Koletzko: “Walking barefoot opens up a new world for the child, especially in summer. It experiences for the first time what sand, grass, gravel, warm or wet ground feels like. It learns to feel the different textures of the ground with its foot. Running over bumps strengthens the muscles, tightens the skeleton, trains the sense of balance and thus makes walking safer”. Around 98% of all babies are born with healthy feet. Even when the child starts to walk, his feet are still normal. From that moment on, however, things often go downhill rapidly. By adulthood, around 60% of people will have foot and posture problems. That means: In more than half of all cases, the feet are really spoiled in childhood.
Supports and insoles often useless
A baby's feet are tiny, delicate and soft. It's hard to imagine that one day they will be able to bear the weight of the body. For this reason, it was believed for a long time that the development had to be aided by proppants. It was the time of insoles, extra strong, high lace-up boots and longer heel caps.
"Today we know that such aids do not promote healthy children's feet, but actually hinder them," says pediatrician Professor Berthold Koletzko. “Children's feet need freedom of movement and a load that the child takes care of itself with its natural urge to move. Children's shoes must therefore be soft and flexible. They must not constrict the feet under any circumstances. It is not the foot that should adapt to the shoe, but the shoe to the foot”.
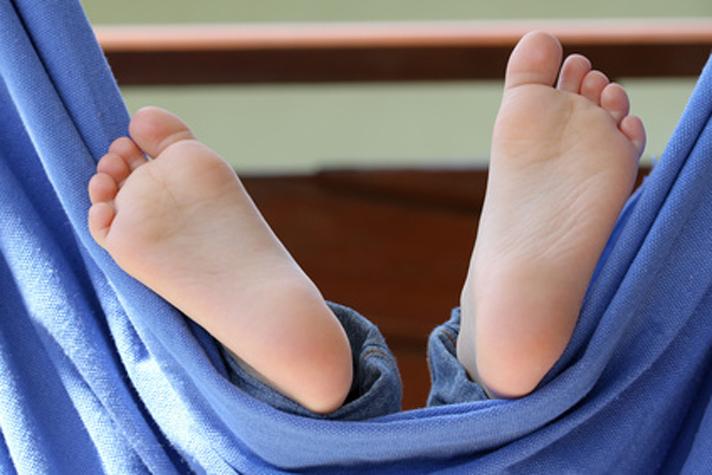

If the shoes are too short and their soles are stiff, they cannot follow the movements of the foot. The middle of the foot falls and the big toe becomes misaligned. Damage to the forefoot occurs as early as infancy, according to the Children's Health Foundation. Appropriate shoes prevent such damage.
Buying to grow – not a healthy trend
Earlier studies of the shoes actually worn by children repeatedly came to the conclusion that half of the children in this country wear shoes that are too small. The results of the measurements for the most recent "German Children's Foot Report" were all the more surprising. The examination of the feet and shoes of 10,773 children between the ages of 0 and 18 by employees of the Institute for Sports Medicine and Prevention at the University of Potsdam revealed that today many children wear shoes that are not too small, but too big! More than 40% of the children walked around in shoes that were one to three sizes larger than the measured foot size. According to the Children's Health Foundation, there are several explanations for the change in trend. The long-standing discussion about children's shoes that are too small could finally have borne fruit and many parents make sure that their children do not walk around in shoes that are too small. The often high price of good children's shoes may also have played a further role: While in the past more parents tried to save on a pair of children's shoes by letting the children run around in shoes that were too small for a while, many parents today try to save a shoe size by buy shoes that are too big.
The high standard of children's shoes offered in Germany is largely due to the WMS measurement system (wide-medium-narrow) introduced in 1974. The system works with design standards for children's shoes that have been jointly agreed upon by paediatricians, orthopedic surgeons and shoe and last manufacturers. They include defined length and width dimensions, but also guidelines regarding the shape, construction and use of materials for children's shoes.
"However, measuring the feet according to the WMS system only makes sense if WMS-standard children's shoes are actually bought afterwards," emphasizes Professor Koletzko. Non-WMS shoes often deviate by one or two shoe sizes from the marked size, usually down. How do you find the right shoe?
The Children's Health Foundation recommends that parents consider the following points when buying shoes:
How many pairs of shoes does a child need?
Since children's feet often grow in phases, you should check every two to three months whether the shoes still fit, recommends the Children's Health Foundation. At the age of two to four years, children's feet grow two to three shoe lengths a year. If a toddler only gets new shoes once a year, they will wear shoes that are too small most of the time.
You cannot rely on the child's information: because they are so soft, children's feet can also be squeezed into shoes that, in extreme cases, are up to five sizes too small, warns the Children's Health Foundation. This forces the toes into misalignments that can permanently damage feet and legs. By the way, there is nothing wrong with passing on little-worn children's shoes, emphasizes the Children's Health Foundation. However, the "inherited" shoes must be long enough and should not be deformed or worn on one side.
Conspicuous feet - harmless or cause for concern?
The flat foot shape of babies has nothing to do with flat feet. Baby feet have a slightly flatter arch because the arch of the foot only develops properly when they learn to walk. However, the main reason they look so flat is because a thick pad of fat hides the bones. It protects the baby's feet from cooling down, but also from overloading. A real flat foot - it is also known as a rocking foot or ink blotter foot - is extremely rare.
Some children are born with one or two sickle feet. The toes are pointing inwards. A treatment is usually unnecessary, or a light foot massage is sufficient for "redress": The outer edge of the foot is gently stroked a few times a day. The heel foot is also harmless (the forefoot points steeply upwards). It almost always goes away on its own. A real bad posture, on the other hand, is clubfoot. It occurs three times in every 1,000 babies, twice as often in boys as in girls, and cannot be corrected manually.
The most important acquired foot damage is splayfoot. It becomes more common with age. Splayfoot is caused by narrowing or persistent compression of the toes in shoes that are too small or too wide. A special form of this foot defect are the crooked toes, but also the claw and hammer toes. Incidentally, the tendency to do so can also be hereditary: splayfoot and crooked toes are more common in certain families than in others.
_____________
(Giulia Roggenkamp, press office, Children's Health Foundation)______Source: idw, press release from the Children's Health Foundation










Test winner at Stiftung Warentest:...
How to get the perfect look for Cos...
Dry elbows: This is how brittle ski...
Cream for Rosacea: The Best Creams