Free access to English version
Peer-review process / manuscript (original) submitted: 28.June 2020 / revised: 21.December 2020
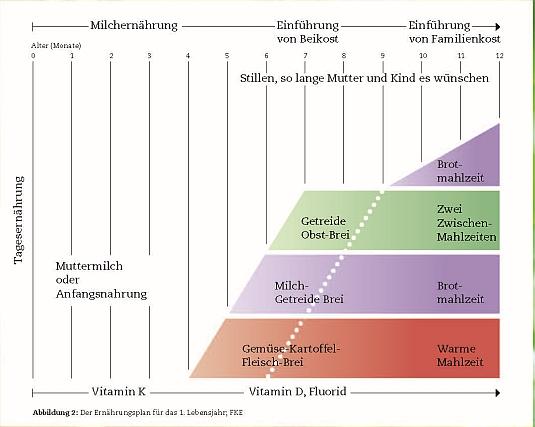
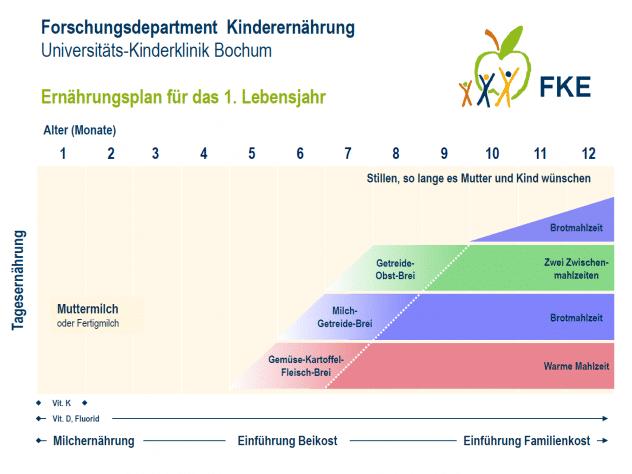
The updated nutrition plan for the 1.age
introduction
In Germany, guidelines for infant nutrition can be attributed to pioneering work of German pediatricians about 120 years ago.The first reasonable assumptions about food needs and a functional diet could be obtained through precise records of food consumption and prosperity [1].These initial rules were continuously developed [2] and a few decades ago by the Research Institute for Children's Nutrition in Dortmund (FKE) to an overall concept as a so -called nutrition plan for the 1.age zusammengefügt [3].
The nutrition plan forms the basis for the corresponding recommendations of the German Society for Pediatric and Adolescent Medicine (DGKJ) and for the recommendations of action of the Young Family network.These are also in accordance with European specialist societies.The plan extensively describes nutritional development in infancy from the exclusive breastfeeding in the first months of life to gradual introduction from complementary foods to the transition to family nutrition, taking into account nutrient requirements, neuromotor development and common foods in Germany.
Abstract
Objective: The update of the nutrition plan for the 1.age des Forschungsdepartment Kinderernährung in Bochum diente dazu, die Umsetzung der aktuellen D-A-CH-Referenzwerte für die Nährstoffzufuhr in der Beikostphase zu überprüfen.Methods: On the basis of a 7-day model feeder for infants aged 8 months, the daily intake of energy and nutrients was calculated and compared with the D-A CH reference values for this age group.The self -production of the complementary meals was based.Standard for the milk, which was consumed in addition to the complementary food, breastfeeding ("breast milk plan") was adopted or consequences as a breast milk substitute ("formula plan").Results: In the updated nutrition plan for the 1.age entspricht die tägliche Zufuhr der meisten Nährstoffe bei beiden Varianten des Plans weitgehend den D-A-CH-Referenzwerten.As a typical finding for nutrition at this age, the supply of the "critical" nutrients iron and iodine is low and the protein intake is high.The different nutrient profiles of meals complement each other to a balanced daily diet.Conclusion: With the new calculations, the modular food and meal-based concept of the nutrition plan for the scientific discussion is disclosed.
Keywords: nutrition plan, complementary food, nutrient intake, meals, child nutrition, infant nutrition
Read this article here free of charge!
https: // creative commons.Org/Licenses/BY-NC-NOD/4.0/legal code
Peer Reviewed / Manuscript (Original) Submitted: 28 June 2020 / Revision Accepted: December 21, 2020
Guidelines for Infant Nutrition in Germany the Updated Dietary Scheme for the First Year of Life
Abstract
Goals: The Updating of the Dietary Scheme for the First Year of Life by the Research Institute of Child Nutrition in Bochum was intended to ensure implementation of the latest German, Austrian and Swiss (D-A-CH) Reference Values for Nutrient Intake During the Compositional Feedingstage.Methodology: On the Basic of a 7-Day Model Dietary Plan for Infants Around the Age of 8 Months, The Daily Intake of Energy and Nutrients was calculated and Compared with a Reference Values for this Age Group.It was assumed that the complementary food (cf) what Prepared at home.The Assumed Standard for the Milk Consumed in Addition to CF Was Breast Milk (“Breast Milk Plan”) Or follow-on Formula as a Substitute for Breast Milk (“Formula Plan”).Results: In the updated Dietary Scheme for the First Year of Life the Daily Intake of Most Nutrients in Both Versions of the Plan Is Largely in Line With D-A-Ch Reference Values.As is a typical finding for nutrition at this agge, the intake of iron and iodine - “critical” Nutrients for this Age Group - is low and protein intake is high.The Different Nutrient Profiles of the Meals Complement Each Other for a Balanced Daily Diet.Conclusion: The New Calculation Open Up The Modular Food and Meal-Based Concept of the Dietary Scheme for Scientific Discussion.
Keywords: Dietary Scheme, Complementary Feeding, Nutrient Intake, Meals, Child Nutrition, Infant Nutrition
Full text PDF (Free version)
https: // creative commons.Org/Licenses/BY-NC-NOD/4.0/legal code
You can also find the full article in nutrition 6/2021 from page M326 to M332.









Test winner at Stiftung Warentest:...
How to get the perfect look for Cos...
Dry elbows: This is how brittle ski...
Cream for Rosacea: The Best Creams